What does a typical day look like for you? It’s facile to fall into a sedentary lifestyle, particularly with a long drive to and from the office, where you sit behind a desk. After work, you drive your kids to practices, and when you finally get home, you are exhausted, so you sit and relax in front of the TV. However, it’s essential to know that serious health risks are associated with sedentary living and physical inactivity.
Our lifestyles have become more sedentary, and this inactivity is taking a toll on our health. But we have the power to change this. It’s necessary to stay active and minimize sedentary behavior for good health and well-being. A sedentary lifestyle involves sitting, reclining, or lying down for extended periods that use little energy.
It’s not just you. Sedentary lifestyles have become the norm for both adults and children. The workweek often entails long hours spent seated at a desk, while commuting is typically sedentary, whether on a bus, train, or car. Even leisure time can revolve around sitting – using a computer or phone, watching TV, or sharing a meal with friends- contributing to our physical inactivity.
What is the Meaning of a Sedentary Lifestyle?
The definition of sedentary behavior is when someone spends more hours per day sitting or lying down and lacks consequential physical movement in their daily life.
Perhaps this scenario rings a bell – you are in an office job, spending the entire workday glued to your chair in front of a computer. Then, you unwind by binge-watching TV shows or scrolling through your phone before hitting the sack. It’s a routine that’s all too easy to slip into, but it’s not without its dangers.

Types of Sedentary Behaviour
1. Occupational Sedentary Behaviour
Desk jobs, work-from-home, and other professionals need prolonged sitting hours.
2. Screen Time Sedentary Behaviour
Excessive usage of electronic gadgets, including watching TV, surfing the internet, playing video games, etc.
3. Transport-related Sedentary Behaviour
Relying on public transport, cars rather than cycling, and walking for transportation.
Also Read: How to Stop Negative Thought? 15 Tips
What has Prompted these Sedentary Habits?
According to a survey by the World Health Organization (WHO) report, 1 out of 4 adults are physically inactive, and 81% of adults lead a sedentary lifestyle.
While our generation has witnessed numerous positive changes in the 21st century, one alarming trend has emerged- a notable shift towards a sedentary lifestyle. This shift is starkly different from the active lifestyles of our grandparents and parents, and a surge in health complications accompanies it.
A few reasons why this inactivity has arrived are:
- Rise in desk jobs coupled with emerging technologies such as laptops and desktops
- Increased amount of time spent on the phone and social media
- Hours spent sitting during commute time to work
- Long work hours, i.e., being a workaholic
- Rise in home delivery cultures has cut down on people’s need to visit stores physically
How Sedentary are we?
An inactive lifestyle contributes to over three million preventable deaths worldwide each year. It is the fourth leading cause of death because of non-communicable diseases.
Further, it’s the cause of 21–25 % of breast and colon cancers, 27% of diabetes, and around 30 percent of ischaemic heart disease.
The National Health Survey results show:
- Nearly one in four people aged 18-64 met the physical activity guidelines.
- Less than one in ten children aged 15-17 follow the recommended daily 60 minutes of physical activity.
- Fewer than one in three children and young people have up to two hours of screen time daily.
- Nearly half of employed people aged 18-64 described their work day as mostly sitting.

Signs You are Living a Sedentary Lifestyle: Health Risks
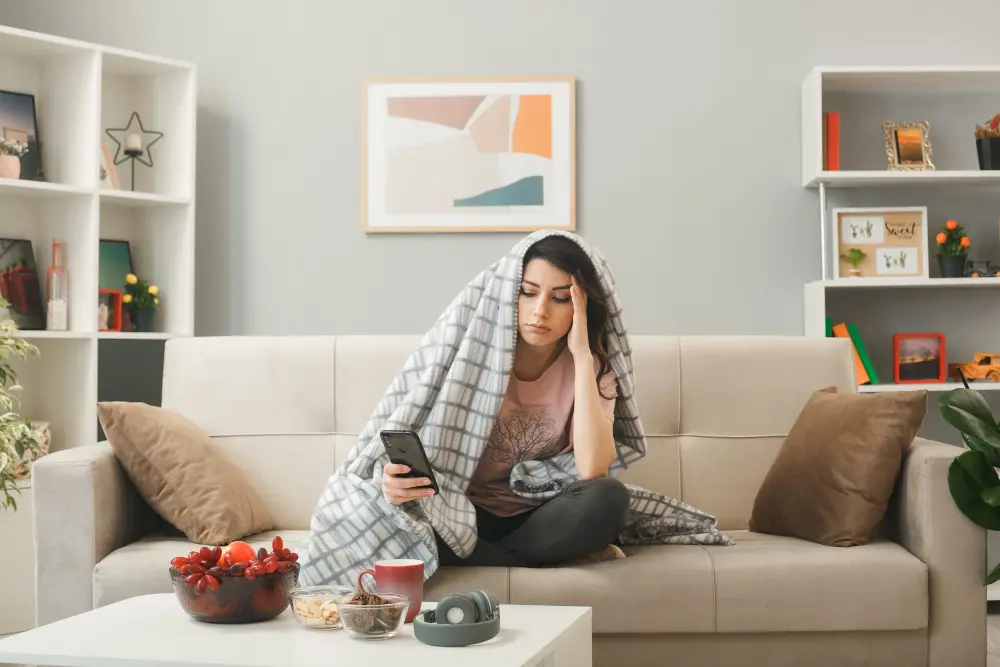

The health risks of sedentary habits can be physical and mental; sometimes, they are so small you may not even recognize them happening to you. It’s essential to understand and acknowledge the signs to make adjustments to improve your health and quality of life.
Some consequences of a sedentary lifestyle that have several adverse long-term effects on our health include:
1. Sleeplessness
If you are not moving much during the day, your body doesn’t feel like it wants to rest and recharge at night, leading to sleep problems. A good dose of exercise helps make you tired in a good way, leading to better sleep.
2. Fatigue
If you are not sleeping at night, that may explain some of your fatigue. However, being sedentary is a significant factor, too. When you are active, your body releases endorphins, bursts of energy, which are mood boosters and pain relievers. You are not releasing endorphins, which could cause fatigue when you are not moving.
Also Read: 30+ Delicious and Healthier Homemade Recipes for Kids
3. Weakened Immunity System
Lack of regular exercise may compromise the immunity system. This makes humans more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
4. Difficulty in Concentrating
Have you found your brain seems a little foggy, or you can’t focus on tasks as well as you used to? Attention, alertness, and motivation can take a big hit without enough physical activity. If you struggle to maintain focus and concentration, read our blog on How to Improve Focus and Concentration? Proven Tips, Activities, and Exercises.
5. Pains and Aches
If sitting at your desk is more painful for your back or neck than it used to be, you probably need to move more.
6. Weight Gain
Working from home is becoming more common, and you may find your clothes snug when you venture into the office. That’s because when you are sedentary, you aren’t burning as many calories, resulting in a little extra weight.
7. Muscle Weakness and Loss
Sitting for extended periods causes muscle weakness and loss. In severe cases, lack of physical activity leads to muscle atrophy and decreased overall muscle mass. This effect of sedentary lifestyle affects the ability to perform everyday activities and increases the risk of falls or injuries.
8. Postural Impact
Prolonged sitting leads to poor posture. This causes the spine to deviate from its natural alignment and movement pattern and can put undue stress on the vertebrae, which leads to subluxations/fixation over time.
Sedentary Lifestyle Solutions
The leading solution to fighting a sedentary lifestyle is incorporating more physical activity. More movement and less sitting contribute to better health. Even some physical activity is better than none.
Moving more combat sedentary behavior and bring about several health benefits, such as:
- Decreased risk of cardiovascular disease and other health and heart conditions
- Reduced risk of being overweight
- Enhanced physical and mental health, such as decreased stress levels
- Improved sleep
- Improved cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels.

Also Read: Mind-Body Relationship (Connection): Benefits and How to Strengthen It?
Recommendations to Make Changes to Sedentary Lifestyle
Do you know if you are sitting too much? Chances are, yes—you are most likely sitting too much. Though you hit the gym for 60 minutes after work daily, your lifestyle is still classified as sedentary in case you spend the rest of your day on your bum.
Embracing an active lifestyle most days of the week and meeting the recommended levels of physical activity for your age group can significantly lessen the health risks of a sedentary lifestyle. For instance, engaging in 60 minutes of physical activity, which can be accomplished through 1 session of 30 minutes and 3 sessions of 10 minutes each, can bring various health benefits.
The good news is an active lifestyle is easily achievable than you might think. All it takes is a little effort to move more and sit less.
1. Active Lifestyle Recommendations for Children Aged 5-27 Years
For kids, an active lifestyle includes participating in the following:
- About 60 minutes per day of moderate-to-vigorous intensity, primarily aerobic physical activity
- At least 3 days a week, incorporate vigorous-intensity aerobic activities and those that strengthen bone and muscle
2. Active Lifestyle Recommendations for People Aged 18-64 Years
For adults, an active lifestyle includes participating in the following:
- About 150 minutes of modest physical activity or at least 75 minutes of robust physical activity
- A combination of moderate and vigorous-intensity activity
- Muscle-strengthening activities on 2 or more days per week
3. Active Lifestyle Recommendations for People Aged 65 Years and Above
The global recommendations for adults aged 18–64 apply to all, with an additional component for those aged 65 and above. This group is encouraged to incorporate a multicomponent physical activity emphasizing functional balance and strength training at moderate or greater intensity 3 or more days a week. This inclusive approach helps enhance functional capacity and prevent falls, regardless of age.
4. Active Lifestyle Recommendations for Individuals Living with Chronic Conditions
The global recommendations for people with a chronic condition, such as diabetes, high BP, or cardiovascular disease, are the same as those for the age group to which they belong.
Prior to starting any new exercise regimen, it is necessary to consult your healthcare professional or doctor. This ensures that you are making informed decisions about your fitness and health and can begin exercising after a cardiac event or diagnosis under the guidance of your healthcare diagnosis.

Tips for an Active Lifestyle
There are multiple ways to become more active and depart from a sedentary lifestyle, from taking part in intentional exercise to making small changes in your daily life to improving incidental exercise.
1. Physical Exercise
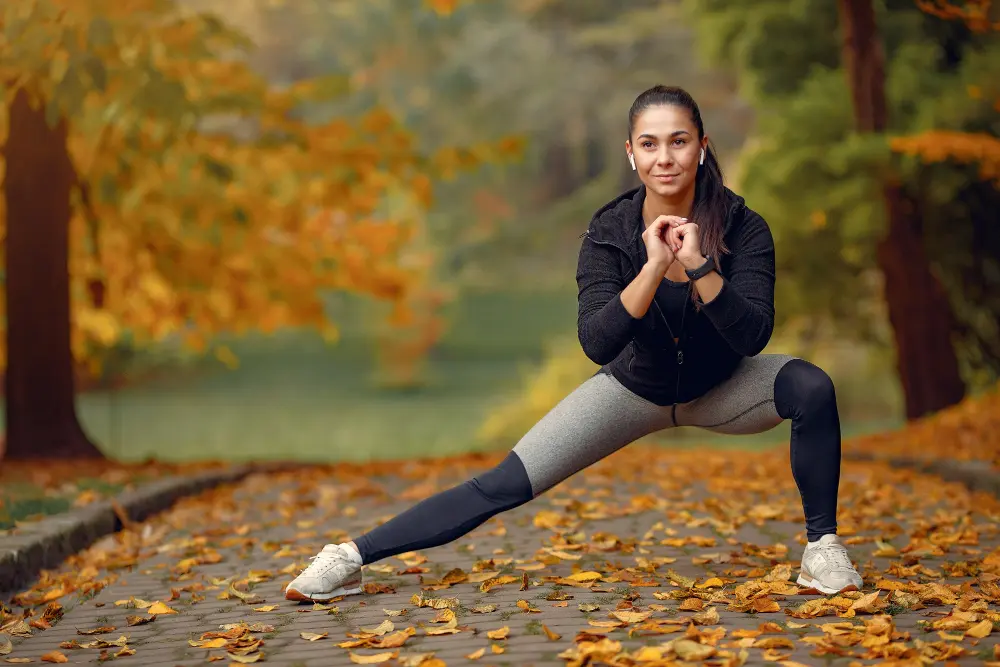

Engaging in cardiovascular exercises that get the heart pumping, such as cycling or running, along with muscle-strengthening exercises like weight training and body-weight exercises, decreases the risks of a sedentary lifestyle.
- Participate in active sporting or leisure activities, such as bushwalking, swimming, yoga, and gym.
- Include exercises that work on core strength. The core muscles are pivotal in stabilizing the spine, and sedentary habits may have impacted core strength.
- If you prefer to exercise at home, you can work out without leaving the house using household items like books and chairs. Also, you can enroll in an online yoga course.
People who choose the proper exercise are likelier to continue yoga programs and physical activities. Adequate warm-up before starting any exercise activity is also essential to avoid injuries.
Also Read: What is Panchakarma? Its Benefits and Treatment
2. Being Active at Study and Work
For many, studying and working are the main contributors to long sitting times.
- Take small breaks from sitting and walk around to stretch your legs.
- Try using a standing desk. You can improvise using a countertop or stacking up books beneath your PC if one is unavailable.
- Conduct walking meetings with colleagues instead of sitting in a room.
3. Reduce Sedentary Behaviour by Boosting Incidental Exercise
- Walk around or stand while talking on the phone and during TV commercials.
- Stand in public transport, or leave one stop earlier and walk the rest.
- Walk up escalators instead of standing, or take the stairs rather than the lift.
- Park away from your landing place and walk the remaining way.
- Look for opportunities to walk during the day, such as walking to a cafe further away than your normal one.
- Try doing the housework or gardening faster to get the heart working more.
Join the online yoga courses by hellomyyoga
Conclusion
Research has linked the effects of a sedentary lifestyle to serious health conditions. Most individuals do not meet the minimum physical activity guidelines and risk developing health issues from too much sedentary time. Human beings can reduce the risks of a sedentary lifestyle by improving their physical activity and using the above techniques to reduce their time sitting.
Our body tends to resist change. Once sprawled on a couch, our body will repel any intention of moving. It is our willpower that keeps us healthy. We have to understand that we were born to move. We can only halt but never stop. The more we move the muscles, we only make them stronger. If you cannot accommodate a disciplined workout in your schedule, make some lifestyle changes.
Read more blogs: